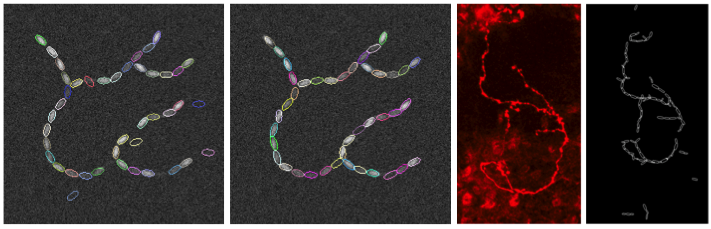
Section: New Results
Cells detection using segmentation competition
Participants : Sen Wang, Emmanuel Soubies, Xavier Descombes.
Marked point processes have proved to be very efficient for segmenting a collection of objects from digital images. The multiple birth and death algorithm provides an optimization framework that allows reasonable time computation. This algorithm has to be embedded in a simluated annealing framework which involves parameters tuning (initial temperature and cooling scheme). This tedious task can be overcame considering a graph cut algorithm instead of the probabilistic death step. The algorithm then consists in successively adding new random objects in the configuration and selecting the most relevant using the graph cut algorithm. In the graph construction a node is associated to each object. In the orignal algorithm proposed by [21] the regularity condition imposed by the graph cut prevents to consider attractive interactions such as clustering or alignment constraints, which restricts the model to repulsive properties such as non overlap between objects. To overcome this restriction we have investigated new graph constructions by considering nodes defined by clusters of interacting objects. Different strategies have been compared to avoid being tracked in local minima defined by clusters while minimizing the number of required iterations. We have applied this new algorithm on different bioimagery problems such as axon extraction or cells detection (see figure 8 ).